In this article, we’ll be covering the different types of navigations and also how to combine them together in react-native using react-navigation 5.
Table Of Content
- Prerequisite
- Project Setup
- Screens Setup
- Installing Dependencies
- Stack Navigator
- Tab Navigator
- Drawer Navigator
- Conclusion
Prerequisite
To be able to follow up with this article, you must have the following setup on your local environment.
Node installed.
An emulator to test the app. You can use either Android Studio or Xcode.
Project Setup
To set up a react-native project, you can make use of the React Native CLI or the Expo CLI.
I would be making use of the Expo CLI to set up a react-native project. To do so, run the following command on your terminal.
1npm install -g expo-cli
The above command would install Expo CLI on your machine.
Note: You need to have Node v12 installed on your machine to be able to install Expo CLI using the command line.
After the above command runs successfully, run the command below to generate/create a react-native project.
1expo init project-name
Once the above command runs successfully, open the project in your desired code editor, and run npm start on the terminal to start the application.
To set up a react-native project using the React-Native CLI, check here.
React Navigation Dependencies & Setup
The dependencies below are the core utility used by the navigators to create the navigation structure, as well as our Stack, Tab, and Drawer navigation.
In your project directory, run the command below on your terminal
1npm install @react-navigation/native @react-navigation/stack @react-navigation/bottom-tabs @react-navigation/drawer
These dependencies below are the dependency relied upon for gestures, animations, and transitions. Also, run the command below on your terminal to install the dependencies.
1npm install react-native-reanimated react-native-gesture-handler react-native-screens react-native-safe-area-context @react-native-community/masked-view
In the root file of our app, in this case, the App.js file, we would set up our react-navigation there.
1// ./App.js23import React from "react";4import { NavigationContainer } from "@react-navigation/native";56const App = () => {7 return <NavigationContainer>{/* Navigation here */}</NavigationContainer>;8};9export default App;
Screens setup
The next step would be to set up screens that would be used in our application.
I would be setting up 3 screens for the purpose of this demo, feel free to just copy them.
I would be setting up 3 screens for the purpose of this demo, feel free to just copy them.
Home Screen
1// ./screens/Home.js23import React from "react";4import { View, Button, Text, StyleSheet } from "react-native";56const Home = () => {7 return (8 <View style={styles.center}>9 <Text>This is the home screen</Text>10 <Button title="Go to About Screen" />11 </View>12 );13};1415const styles = StyleSheet.create({16 center: {17 flex: 1,18 justifyContent: "center",19 alignItems: "center",20 textAlign: "center",21 },22});2324export default Home;
About Screen
1// ./screens/About.js23import React from "react";4import { View, StyleSheet, Text } from "react-native";56const About = () => {7 return (8 <View style={styles.center}>9 <Text>This is the about screen</Text>10 </View>11 );12};1314const styles = StyleSheet.create({15 center: {16 flex: 1,17 justifyContent: "center",18 alignItems: "center",19 textAlign: "center",20 },21});2223export default About;
Contact Screen
1// ./screens/Contact.js23import React from "react";4import { View, StyleSheet, Text } from "react-native";56const Contact = () => {7 return (8 <View style={styles.center}>9 <Text>This is the contact screen</Text>10 </View>11 );12};1314const styles = StyleSheet.create({15 center: {16 flex: 1,17 justifyContent: "center",18 alignItems: "center",19 textAlign: "center",20 },21});2223export default Contact;
Stack Navigation
Stack navigation provides a way for react-native apps to transition between screens by using a stack, which means the screens are stacked on each other.
For example, if you navigate from login to signup screen, the signup screen is stacked on top of the login screen, and if you navigate back, the signup screen is then popped off the stack.
To set up the stack navigation, I’d create a navigation directory at the root of our project. Inside our newly created directory, I’d also create a StackNavigator.js file in there, and add our stack navigation setup.
Note: You can decide to name the folders and files however you want
1// ./navigation/StackNavigator.js23import React from "react";4import { createStackNavigator } from "@react-navigation/stack";56import Home from "../screens/Home";7import About from "../screens/About";89const Stack = createStackNavigator();1011const MainStackNavigator = () => {12 return (13 <Stack.Navigator>14 <Stack.Screen name="Home" component={Home} />15 <Stack.Screen name="About" component={About} />16 </Stack.Navigator>17 );18};1920export { MainStackNavigator };
You can also customize and style the stack navigation by adding screenOptions props style, see basic example below
1// ./navigation/StackNavigator.js23const MainStackNavigator = () => {4 return (5 <Stack.Navigator6 screenOptions={{7 headerStyle: {8 backgroundColor: "#9AC4F8",9 },10 headerTintColor: "white",11 headerBackTitle: "Back",12 }}13 >14 <Stack.Screen name="Home" component={Home} />15 <Stack.Screen name="About" component={About} />16 </Stack.Navigator>17 );18};
Back in our App.js file, we can import and add our newly created Stack Navigator. So our App.js file would look like the code below
1// ./App.js23import React from "react";4import { NavigationContainer } from "@react-navigation/native";56import { MainStackNavigator } from "./navigation/StackNavigator";78const App = () => {9 return (10 <NavigationContainer>11 <MainStackNavigator />12 </NavigationContainer>13 );14};15export default App;
Now if we run the code on our emulator, We should now see our Home screen rendering on our Stack screens.
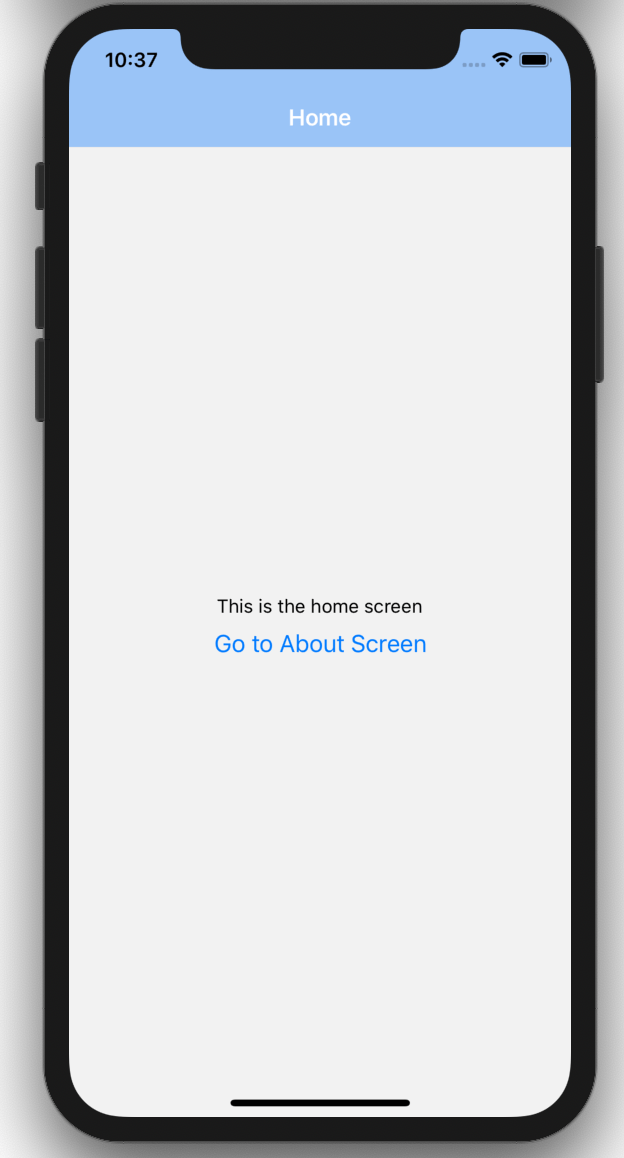
Remember in our ./screens/Home.js file, we had a button that did nothing, but since we have our stack navigation setup, we can now have access to navigation prop injected by the stack navigation which can help us perform many operations, one of which is redirecting.
So navigate to ./screens/Home.js and add the code below.
1// ./screens/Home.js23import React from "react";4import { View, Button, Text, StyleSheet } from "react-native";56const Home = ({ navigation }) => {7 return (8 <View style={styles.center}>9 <Text>This is the home screen</Text>10 <Button11 title="Go to About Screen"12 onPress={() => navigation.navigate("About")} // We added an onPress event which would navigate to the About screen13 />14 </View>15 );16};1718const styles = StyleSheet.create({19 center: {20 flex: 1,21 justifyContent: "center",22 alignItems: "center",23 textAlign: "center",24 },25});2627export default Home;
In the code above, we get the navigation prop, which is an object that has a navigate function which we then call passing in the name of the screen we want to navigate to after the button is pressed.
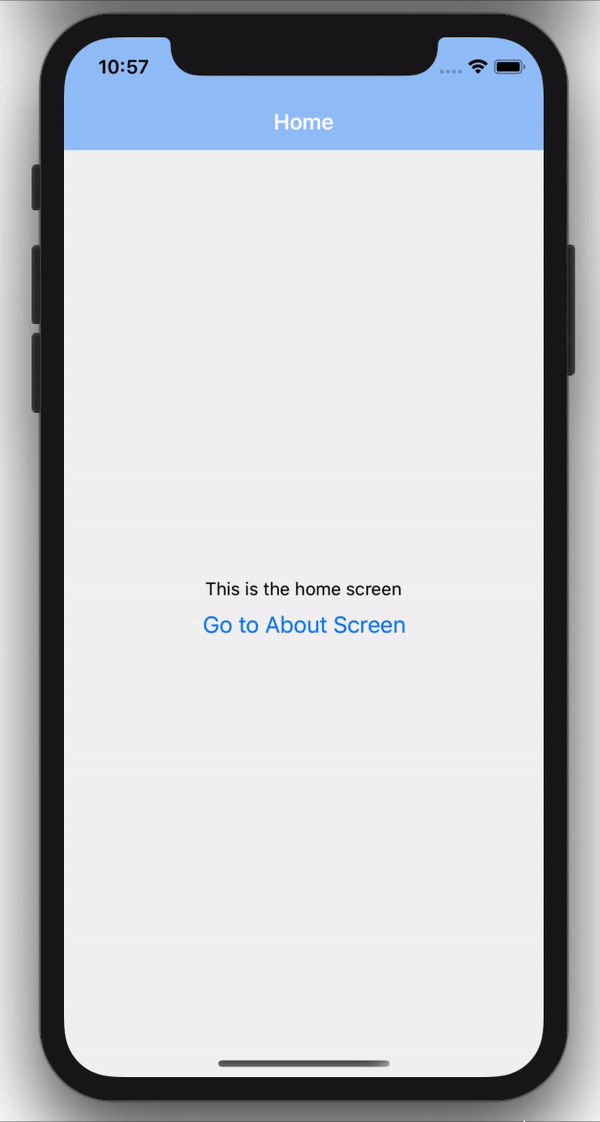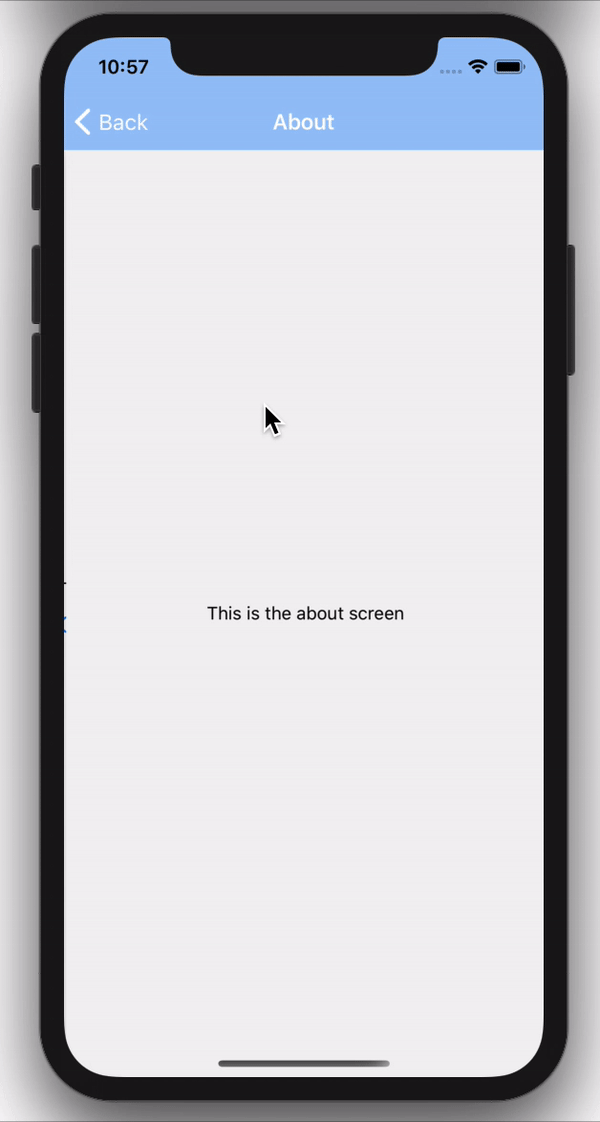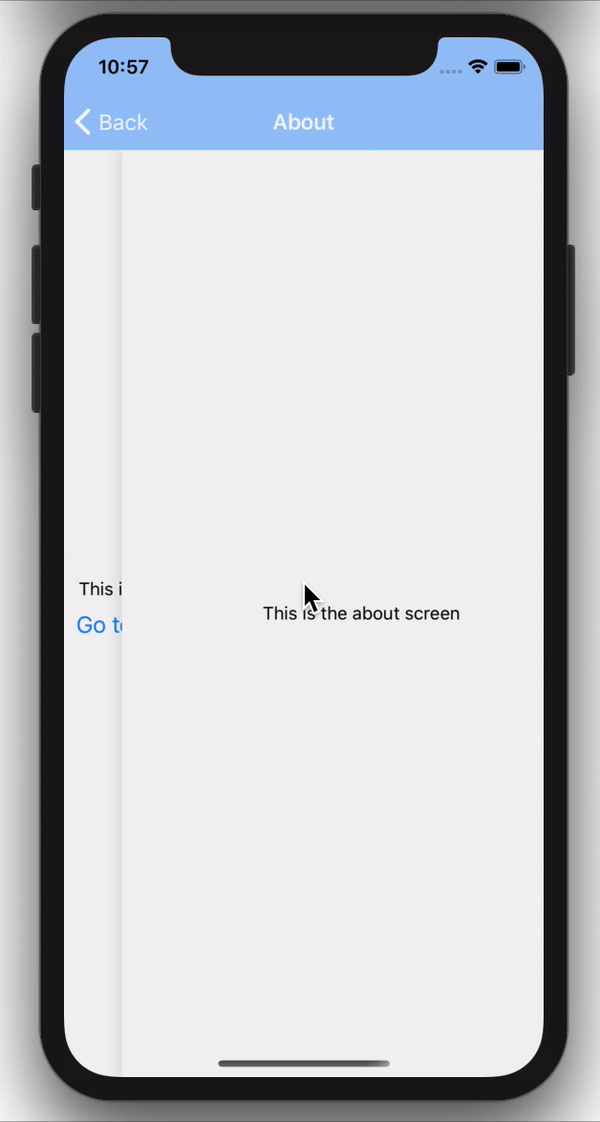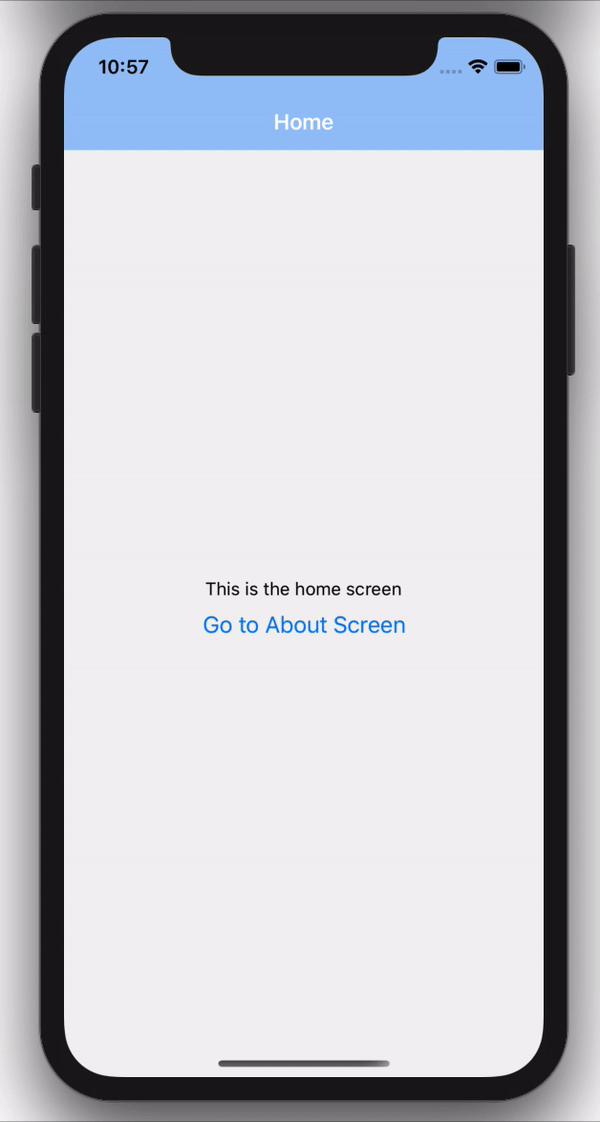
And there we have it, we can now navigate between screens using our stack navigation.
Tab Navigation
Tab navigation is a navigation that is tabbed at either the bottom or top of a screen and can be used to switch between different screens.
Tab navigation can take in either the screen as a component or a Stack as the component.
In our StackNavigator.js file, let’s create another stack for our contact screen. So our StackNavigator.js will look like below
1// ./navigation/StackNavigator.js23import React from "react";4import { createStackNavigator } from "@react-navigation/stack";56import Home from "../screens/Home";7import About from "../screens/About";8import Contact from "../screens/Contact";910const Stack = createStackNavigator();1112const screenOptionStyle = {13 headerStyle: {14 backgroundColor: "#9AC4F8",15 },16 headerTintColor: "white",17 headerBackTitle: "Back",18};1920const MainStackNavigator = () => {21 return (22 <Stack.Navigator screenOptions={screenOptionStyle}>23 <Stack.Screen name="Home" component={Home} />24 <Stack.Screen name="About" component={About} />25 </Stack.Navigator>26 );27};2829const ContactStackNavigator = () => {30 return (31 <Stack.Navigator screenOptions={screenOptionStyle}>32 <Stack.Screen name="Contact" component={Contact} />33 </Stack.Navigator>34 );35};3637export { MainStackNavigator, ContactStackNavigator };
We can then create another file TabNavigator.js in the navigations directory and add the markup for our TabNavigator
1// ./navigation/TabNavigator.js23import React from "react";4import { createBottomTabNavigator } from "@react-navigation/bottom-tabs";56import { MainStackNavigator, ContactStackNavigator } from "./StackNavigator";78const Tab = createBottomTabNavigator();910const BottomTabNavigator = () => {11 return (12 <Tab.Navigator>13 <Tab.Screen name="Home" component={MainStackNavigator} />14 <Tab.Screen name="Contact" component={ContactStackNavigator} />15 </Tab.Navigator>16 );17};1819export default BottomTabNavigator;
And then back in our App.js file, we can now import our newly created TabNavigator and use it there.
1// ./App.js23import React from "react";4import { NavigationContainer } from "@react-navigation/native";56import BottomTabNavigator from "./navigation/TabNavigator";78const App = () => {9 return (10 <NavigationContainer>11 <BottomTabNavigator />12 </NavigationContainer>13 );14};15export default App;
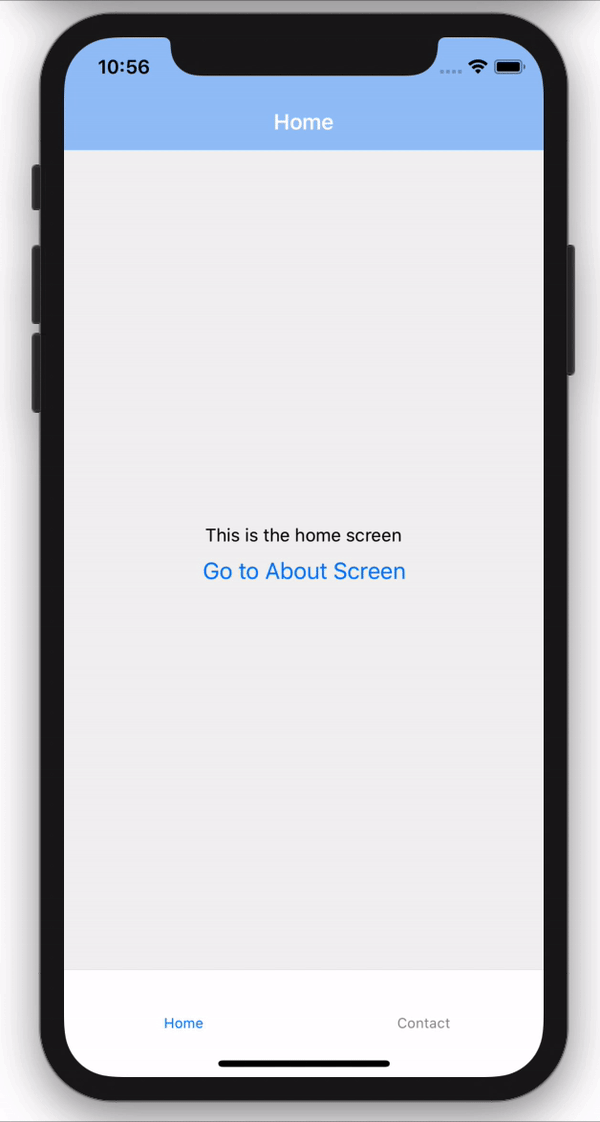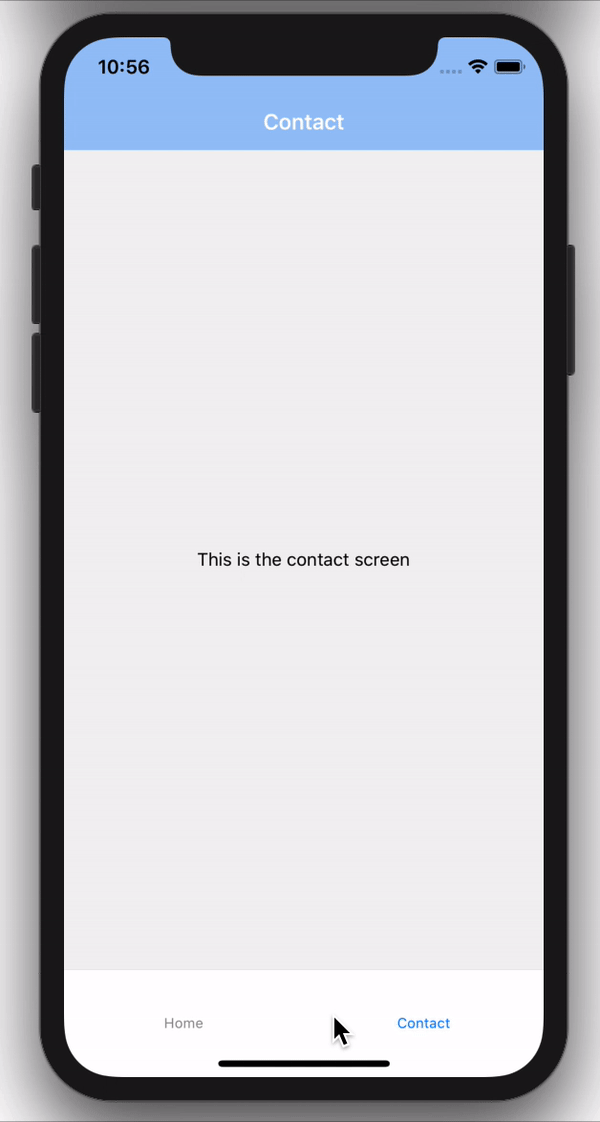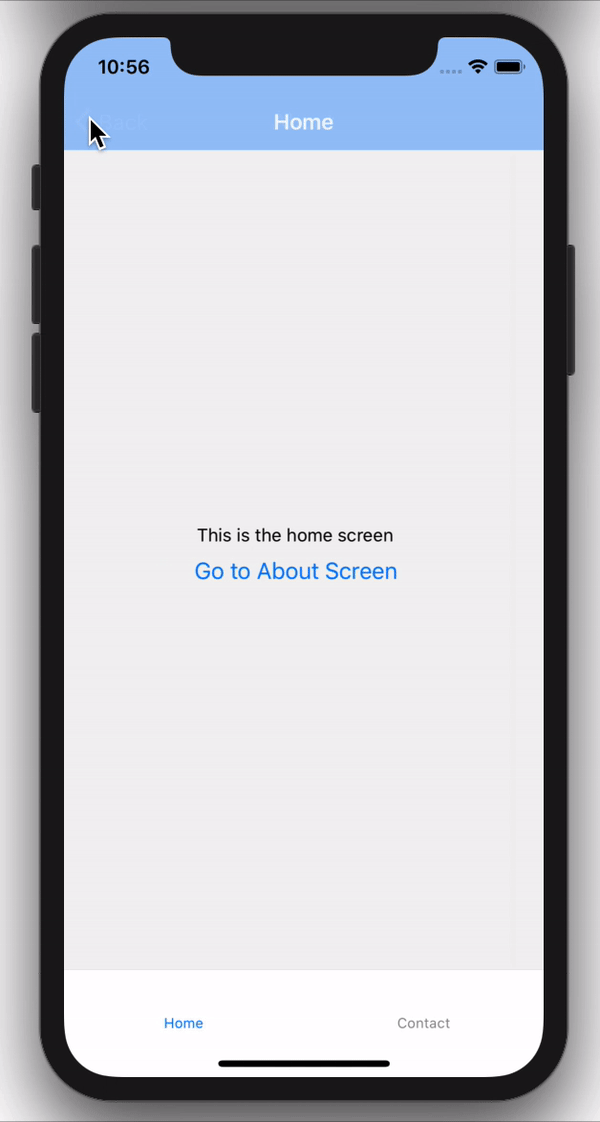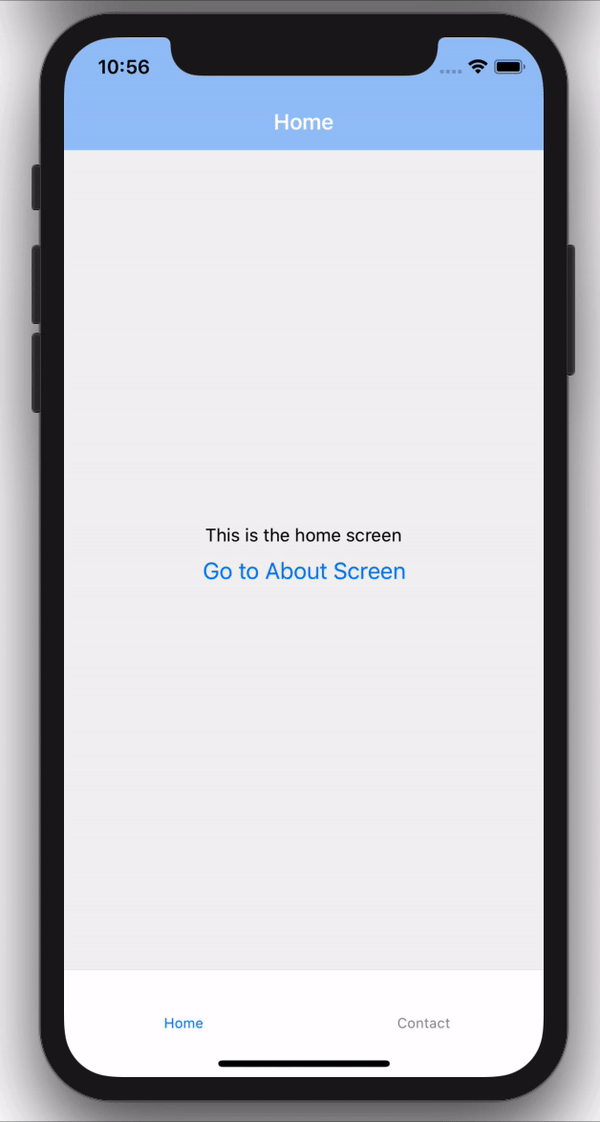
Drawer Navigation
Drawer navigation is a slide-out and slide-in drawer that contains links to various screens. The Drawer navigation opens when a menu icon is clicked or when a user swipes their finger from the left or right edge of the app.
In order to create drawer navigation, we would create another file in our navigations directory called DrawerNavigator.js
In that file, we would add our drawer navigator markup
1// ./navigation/DrawerNavigator.js23import React from "react";45import { createDrawerNavigator } from "@react-navigation/drawer";67import { ContactStackNavigator } from "./StackNavigator";8import TabNavigator from "./TabNavigator";910const Drawer = createDrawerNavigator();1112const DrawerNavigator = () => {13 return (14 <Drawer.Navigator>15 <Drawer.Screen name="Home" component={TabNavigator} />16 <Drawer.Screen name="Contact" component={ContactStackNavigator} />17 </Drawer.Navigator>18 );19};2021export default DrawerNavigator;
And then back in our App.js file, we can now import our newly created DrawerNavigtor.js file and use it as our navigator.
1// ./App.js23import React from "react";4import { NavigationContainer } from "@react-navigation/native";56import DrawerNavigator from "./navigation/DrawerNavigator";78const App = () => {9 return (10 <NavigationContainer>11 <DrawerNavigator />12 </NavigationContainer>13 );14};15export default App;
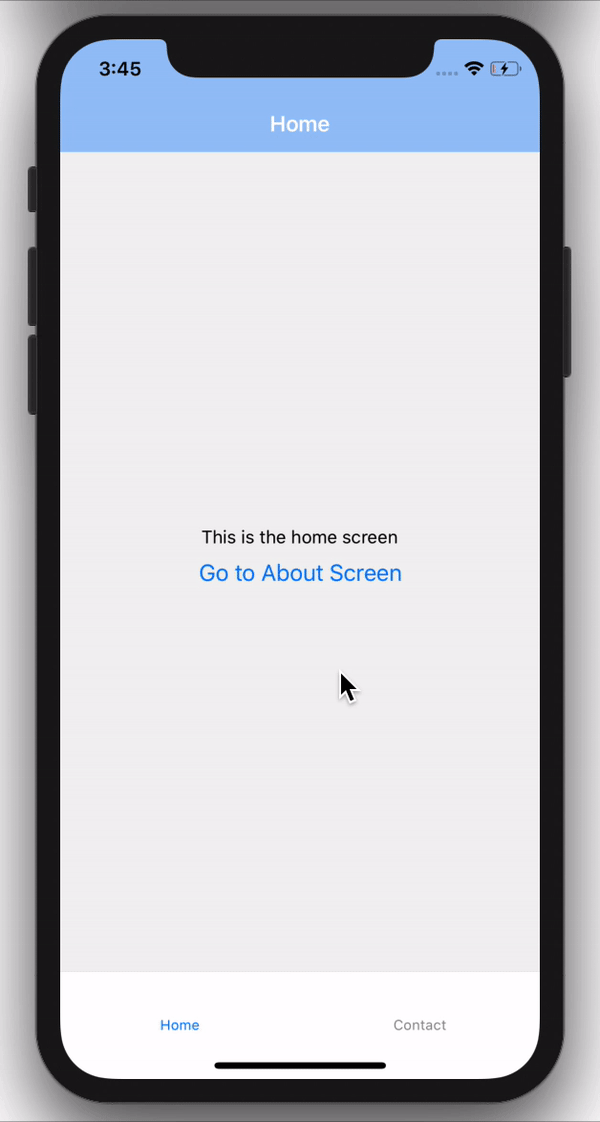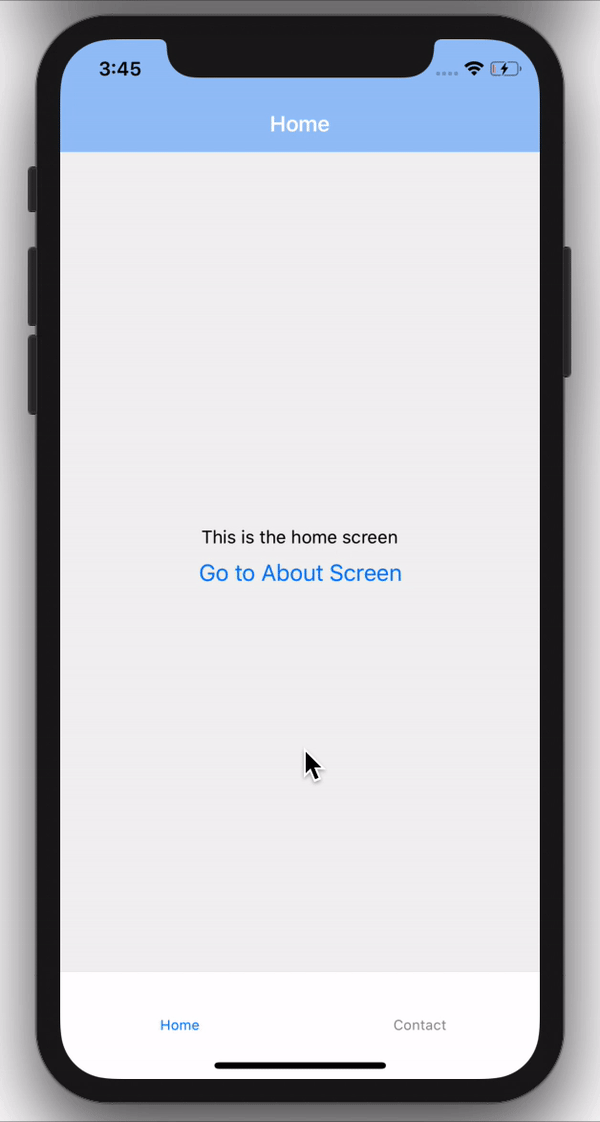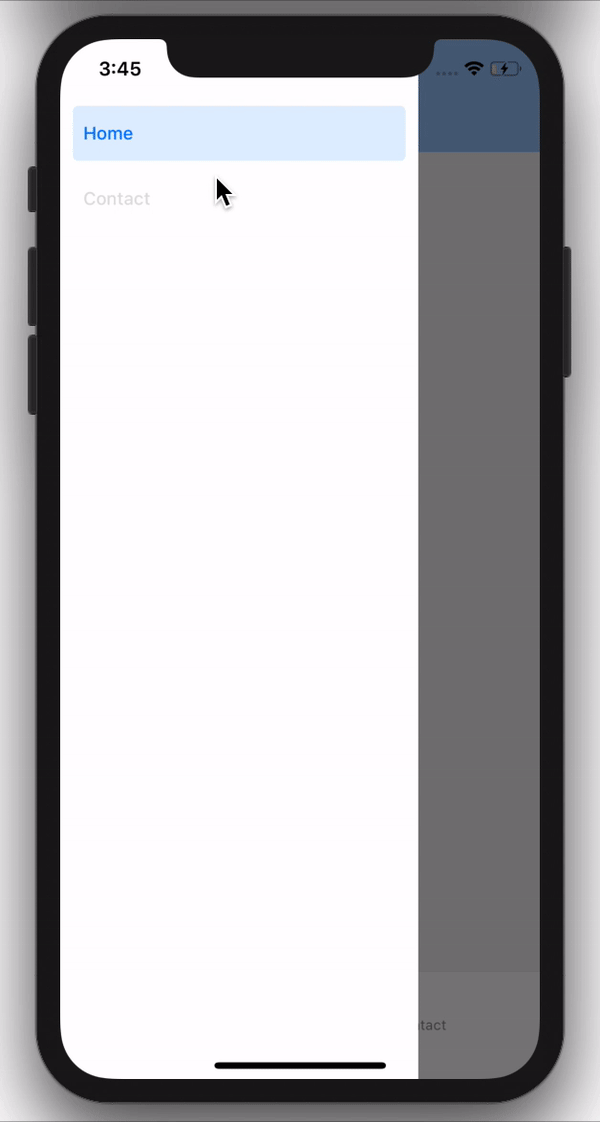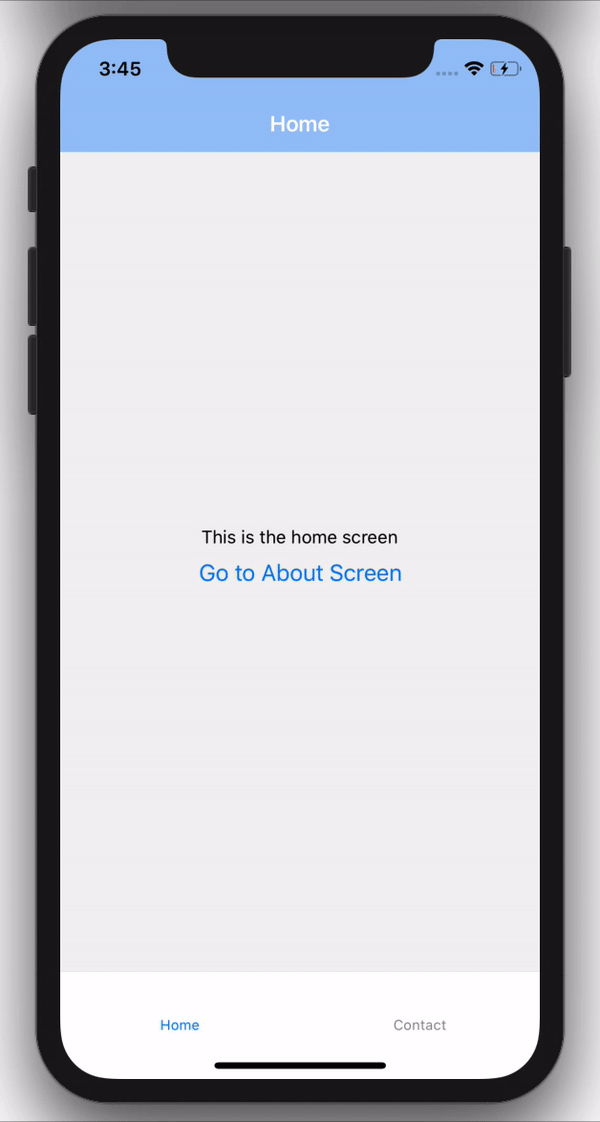
There are also configuration options and header icons you can add to customize your drawer navigation. Find out more here.
Conclusion
In this article, we’ve been able to look at how to set up and combine the Stack, Tab and Drawer navigation for our react-native app using react-navigation 5.
The source code used in demonstrating this article can be found here.
If you have any questions or feedback about this article, feel free to reach out.
Thanks for reading.